Archives
- 2026-02
- 2026-01
- 2025-12
- 2025-11
- 2025-10
- 2025-09
- 2025-03
- 2025-02
- 2025-01
- 2024-12
- 2024-11
- 2024-10
- 2024-09
- 2024-08
- 2024-07
- 2024-06
- 2024-05
- 2024-04
- 2024-03
- 2024-02
- 2024-01
- 2023-12
- 2023-11
- 2023-10
- 2023-09
- 2023-08
- 2023-07
- 2023-06
- 2023-05
- 2023-04
- 2023-03
- 2023-02
- 2023-01
- 2022-12
- 2022-11
- 2022-10
- 2022-09
- 2022-08
- 2022-07
- 2022-06
- 2022-05
- 2022-04
- 2022-03
- 2022-02
- 2022-01
- 2021-12
- 2021-11
- 2021-10
- 2021-09
- 2021-08
- 2021-07
- 2021-06
- 2021-05
- 2021-04
- 2021-03
- 2021-02
- 2021-01
- 2020-12
- 2020-11
- 2020-10
- 2020-09
- 2020-08
- 2020-07
- 2020-06
- 2020-05
- 2020-04
- 2020-03
- 2020-02
- 2020-01
- 2019-12
- 2019-11
- 2019-10
- 2019-09
- 2019-08
- 2019-07
- 2019-06
- 2019-05
- 2019-04
- 2018-11
- 2018-10
- 2018-07
-
Functionally all members of the IL family have been
2019-07-25
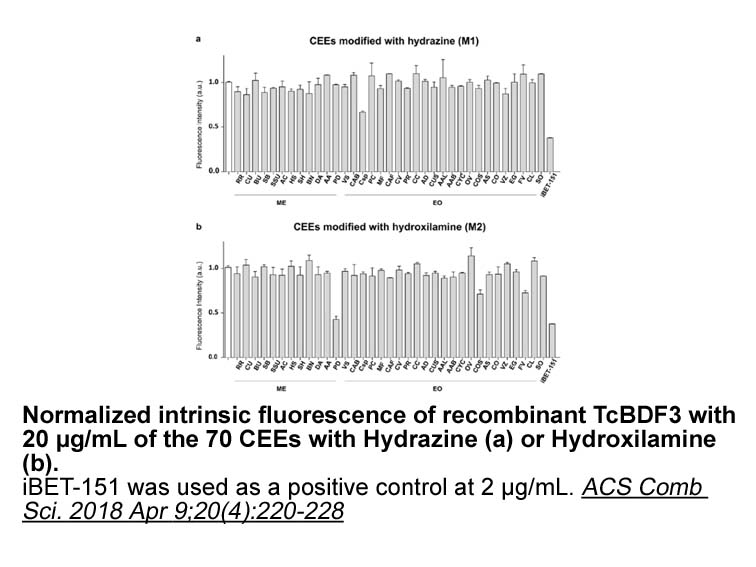
Functionally, all members of the IL-12 family have been annotated along major inflammatory signaling axes but their roles have often weighed on opposing sides of the immunological balance. For instance, IL-12 and IL-23 are classified as pro-inflammatory cytokines [10] as opposed to the rather protec
-
It is worth mentioning that in this
2019-07-25
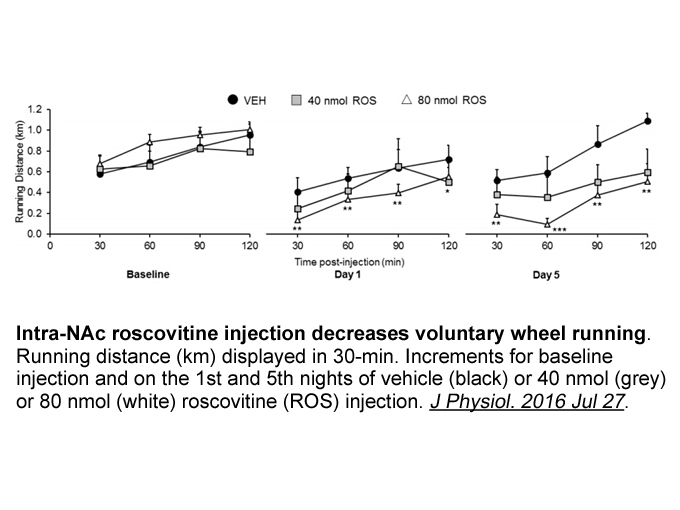
It is worth mentioning that, in this study we only observed the responses of CYP450 to the short-term exposure of DSP toxins (12 h). However, the toxic effects of DSP toxins to bivalves appeared to abate with longer exposure (Pinto-Silva et al., 2005; Flórez-Barrós et al., 2011; Prego-Faraldo et al.
-
br Methods br Results br Discussion The lowest intra CeA
2019-07-25
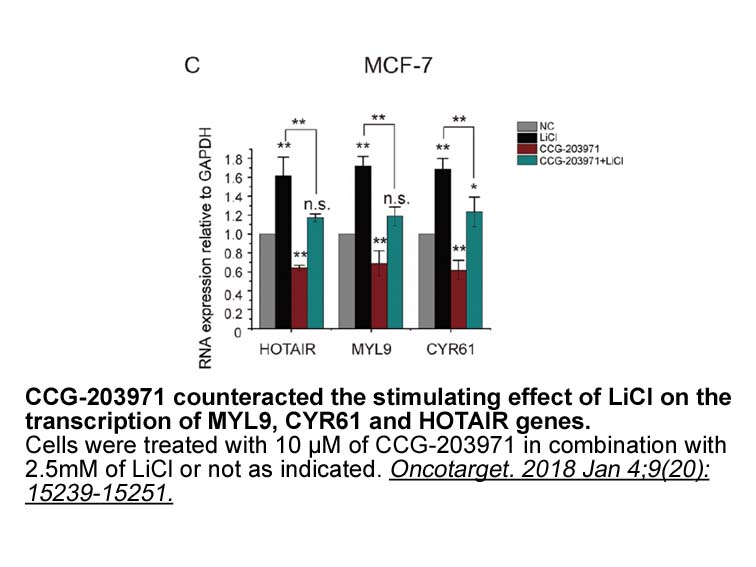
Methods Results Discussion The lowest intra-CeA dose of R278995/CRA0450 that prevented the elevations in monensin reward thresholds associated with nicotine withdrawal was 0.05μg/side (0.1μg total bilateral dose). The total bilateral dose in the present study is 100 times lower than the low
-
br Acknowledgment br Introduction Pesticides
2019-07-25
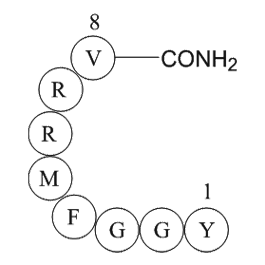
Acknowledgment Introduction Pesticides are largely used in agriculture to enhance food production and, to a lesser extent, to control unwanted pests and disease vectors in public health. However, these compounds are often associated with toxicity in non-target species including humans. Occupat
-
br Results and discussion Compounds were tested for
2019-07-24
Results and discussion Compounds were tested for their binding affinity to human CRTH2 in a radioligand binding assay (3H-PGD2) using CHO cells stably transfected with human CRTH2. In addition, these compounds were assessed for their functional activity in PGD2 driven Ca2+ flux in KB8 cells expre
-
Mifepristone br Collagens as new drivers of zebrafish tissue
2019-07-24
Collagens as new drivers of zebrafish tissue regeneration Contrary to mammals, zebrafish possess very high regeneration capacities and thereby represent a versatile model to study tissue and organ regeneration. Adult fish can fully reconstruct their brain, spinal cord, retina, kidney, liver, panc
-
What is the predominant mechanism underlying the benefits
2019-07-24
What is the predominant mechanism underlying the benefits of udenafil, i.e. the vascular vs. myocardial effect? Lewis et al. suggested that the benefit of sildenafil in HFrEF would be derived from augmented RV systolic function that mainly results from pulmonary vasodilation, suggestive of the ‘vasc
-
WIN 64338 hydrochloride Thus RhoA mediated inhibition of DGK
2019-07-24
Thus RhoA-mediated inhibition of DGKθ is a well-characterized pathway, conserved from C. elegans to mammalian tissues, which enables G-protein coupled receptors to regulate the extent and kinetics of DAG-mediated signaling by fine tuning DGK enzymatic activity. Acknowledgments Introduction Ce
-
The outcome of DGK function will thus depend
2019-07-24
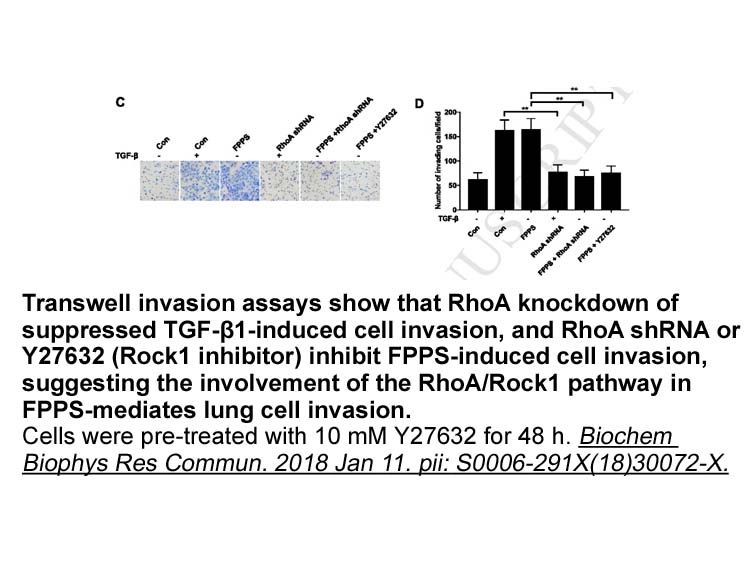
The outcome of DGK function will thus depend on the binding partners of each DGK isoform, and the effects that they exert can be quite different. A clear example of this concept has been demonstrated for the type IV DGKs, ζ and ι, which are structurally very similar but have opposing effects on Ras
-
DGK deficiency caused a significant increase in the SERT pro
2019-07-24
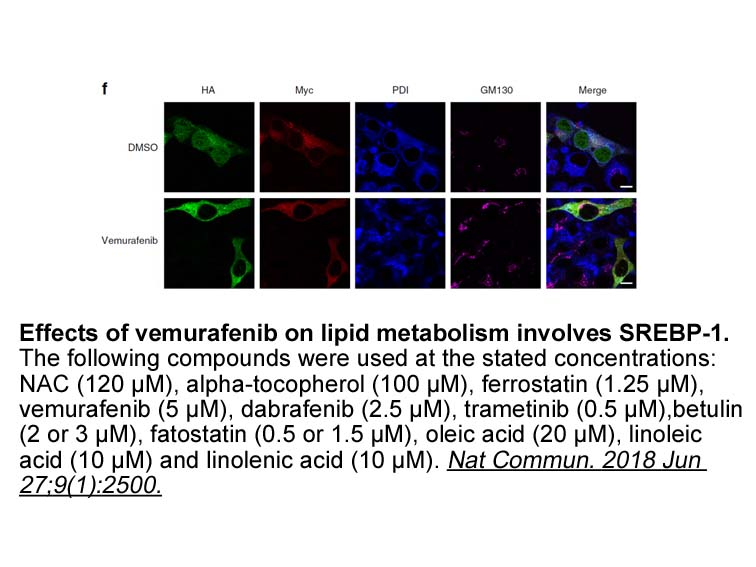
DGKδ deficiency caused a significant increase in the SERT protein level, but its mRNA level was not affected (Fig. 1). These results suggest that SERT protein stability is directly reduced by interaction with the DGKδ protein. In contrast, DGKδ deficiency regulated both TPH-2 and MAO-A protein and
-
br Conclusions Present work comprehensively characterizes th
2019-07-24
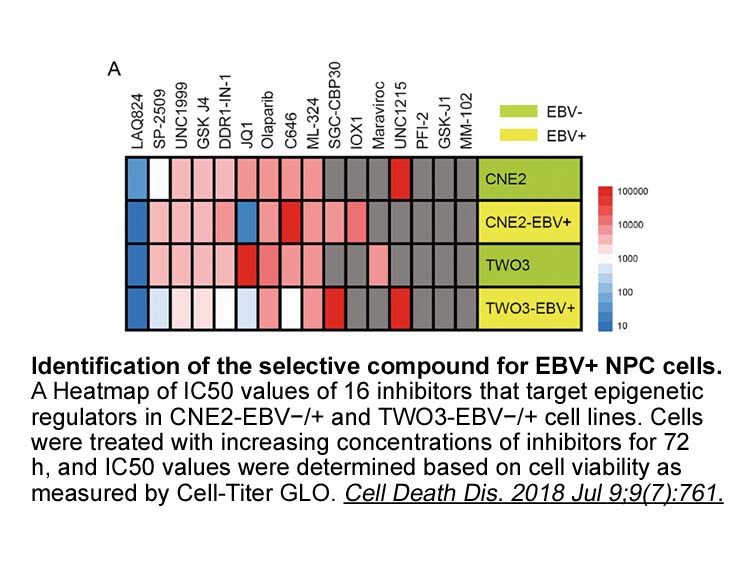
Conclusions Present work comprehensively characterizes the inhibitory activity of Yersinia enterocolitica against cysteine proteases. All tested strains, regardless of their bioserotype, genotype and the presence of virulence markers, synthesized the high-molecular-weight inhibitors of papain and
-
br Methods br Results br
2019-07-24
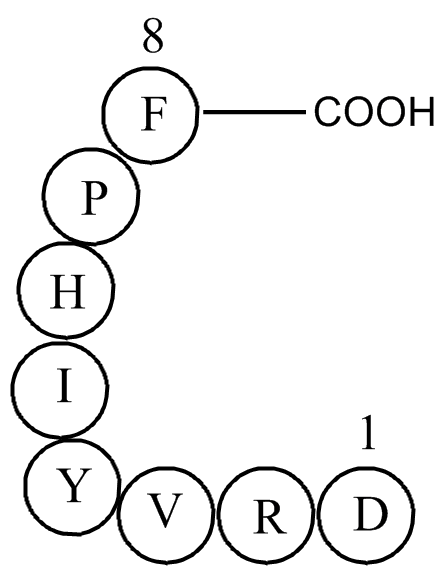
Methods Results Discussion MEN91507 is a potent and selective CysLT1 receptor antagonist. Guinea-pig lung membranes have been widely used for the detection and characterization of CysLT1 receptor antagonists: in this assay the high affinity (subnanomolar) binding of [3H[leukotriene D4 or [3
-
Cot MAP K is the
2019-07-24
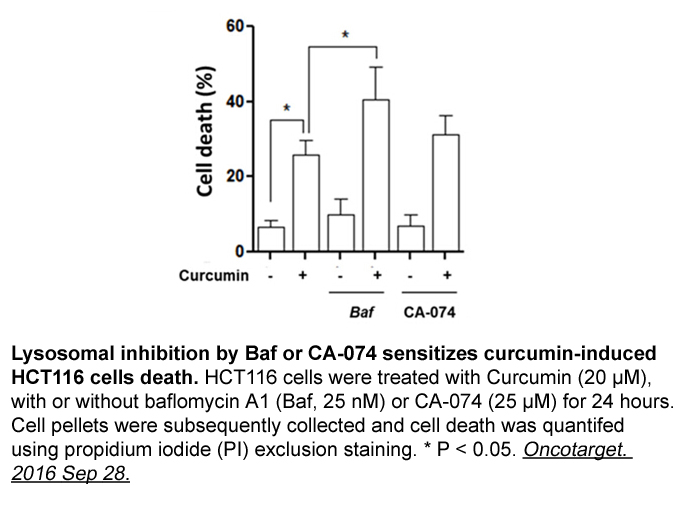
Cot (MAP3K8) is the sole MAP3K that activates the MEK1/2-Erk1/2 following the activation of the TLR/IL-1 receptor superfamily as well as some receptors of the TNF receptor family [8], [9], [10] and mediates the production of chemokines and cytokines in different cell systems [reviewed in [11]]. Thus
-
TCS 2002 It is interesting to note
2019-07-24
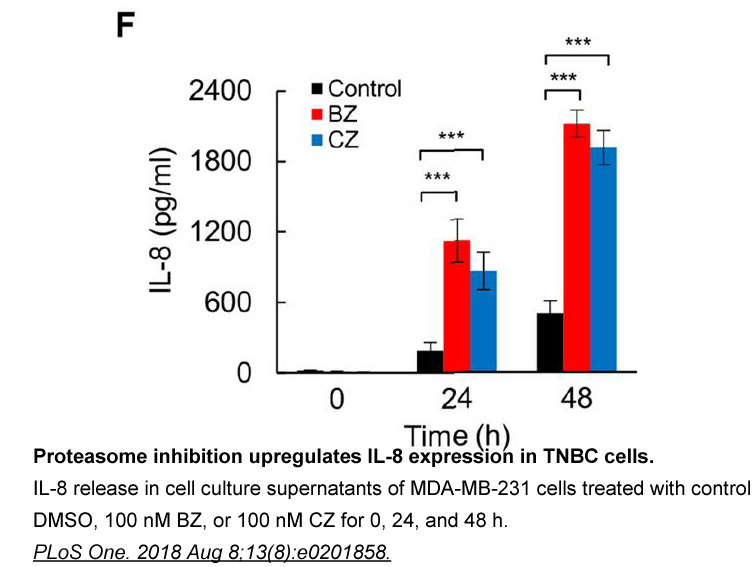
It is interesting to note that Eibinger and colleagues [23] recently reported chemotactic movement to 25-OHC in THP1 cells as well as in primary human monocytes. RNA interference suggested that in part this migration was mediated by EBI2. Competing financial interest statement Acknowledgments
-
In summary the metabolism of GEF
2019-07-23
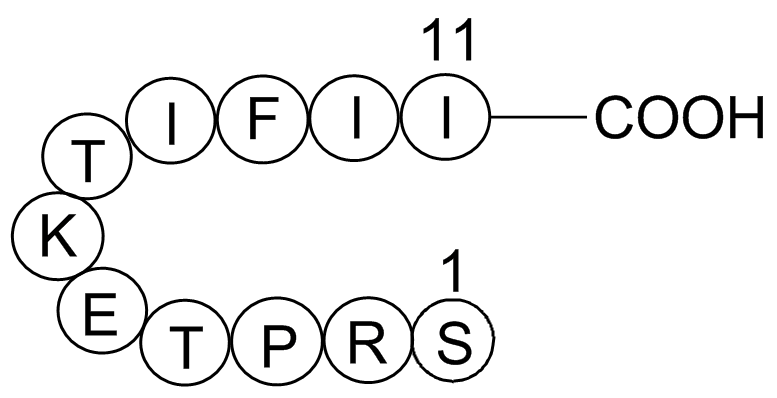
In summary, the metabolism of GEF in HLM and MLM was extensively studied using a LC–MS-based metabolomic approach. This study identified a total of 34 metabolites and adducts related to GEF (Fig. 10) and identified three new potential reactive metabolites, including two aldehydes and one iminium. Pr
16552 records 1029/1104 page Previous Next First page 上5页 10261027102810291030 下5页 Last page